
Occasionally, immunity wanes and women benefit from a pre-pregnancy MMR booster. When you see your doctor for a preconception visit, they can check to see if you're still immune from your childhood MMR vaccine.

In other cases, heart problems may run in families. In most cases, though, doctors don't know why specific congenital heart defects happen. Some congenital heart defects may be related to a disease the mother has, such as diabetes. Some things – like some congenital heart defects – are largely out of your control.

But it's not a guarantee that nothing will go wrong. It's important to do everything you can to stay healthy before and during pregnancy.
NORMAL HEARTBEAT FOR 12 WEEK FETUS HOW TO
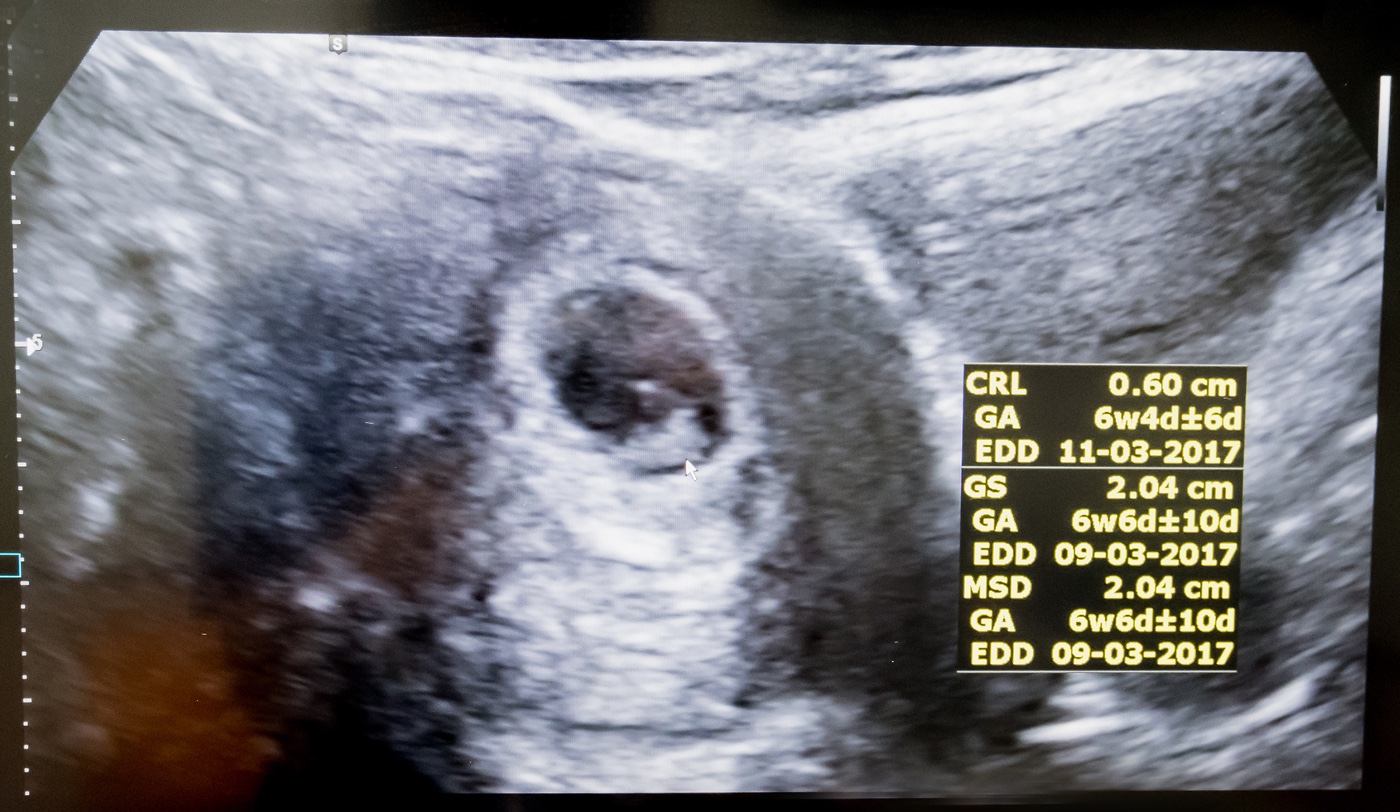
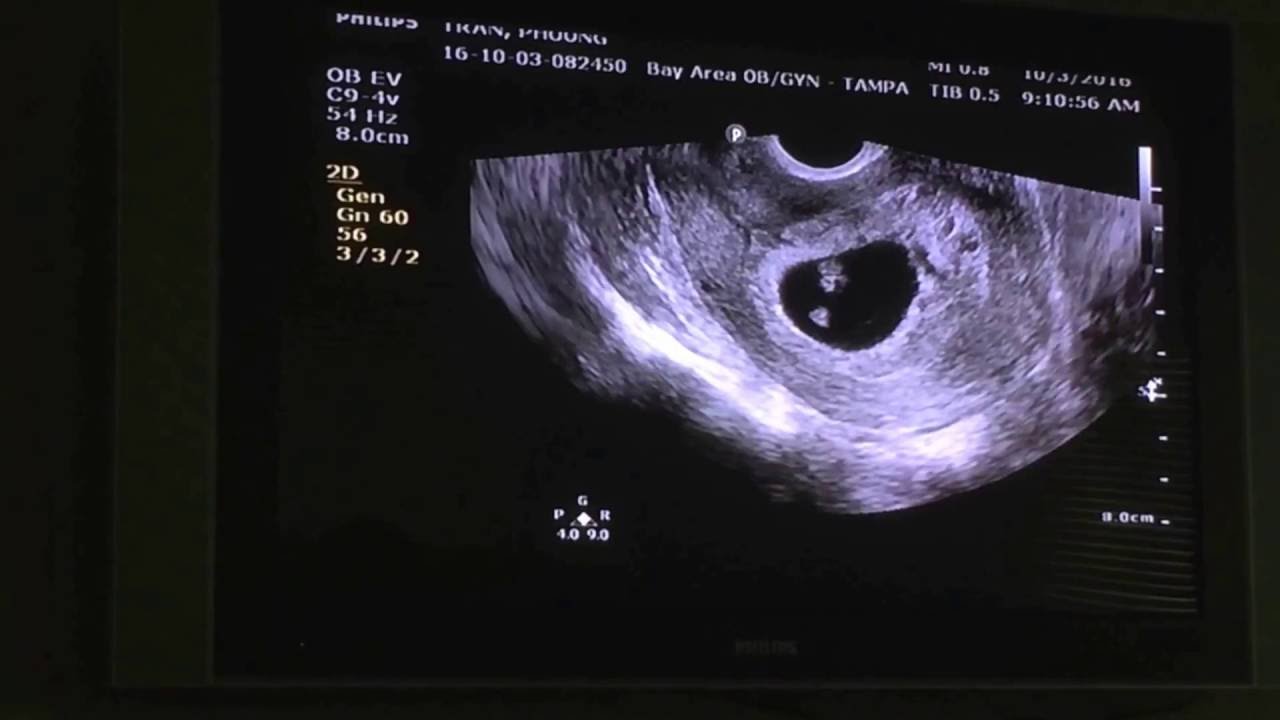
How to support your baby’s heart before and during pregnancy Your obstetrician or midwife will talk with you about what your individual ultrasound means and what your next steps are. This means that the fertilized egg isn't developing. (This is common!) If there's a "fetal pole" (visible embryo) and no heart motion, it's possible that you have a "missed miscarriage" or blighted ovum. If at your first ultrasound your provider can't see the future heart pulsating, it may simply be that your dating is off and it's too soon to see the heart motion. This ultrasound can also be used to screen for heart problems, which may be important if there's a family history of congenital heart problems. If you have a first trimester ultrasound (perhaps because you've had a previous pregnancy complication), it's possible to see cardiac activity this early. When can you see your baby's heartbeat?Īround 4 weeks after conception, or 6 weeks after your last menstrual period, the fast flickering of the embryo's developing heart tube can be seen on ultrasound. For this reason, the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecologists (ACOG) defines the fluttering of cells in the embryonic heart tube as "cardiac activity" rather than a heartbeat. When you're 6 weeks pregnant, however, the heart isn't fully developed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
